区块链到简单虚拟货币
区块链技术旨在实现并维持一个去中心化的点对点网络系统以及其中附带的功能,虚拟货币就是其中之一。
什么是区块链?
区块链根据语义能有不同含义:
一种数据结构
一种算法
一个完整的技术方案
一个完全去中心化的点对点系统
当作为数据结构时,它表现为区块和链等多个形式
const getSha=require("crypto-js/sha256")
class EzBlock {
constructor(data,previousHash){
this.data=data;
this.previousHash=previousHash;
this.hash=this.createHash();
}
createHash(){
return getSha(this.data+this.previousHash).toString();
}
}
class EzChain {
constructor(){
this.chain=[this.bigbang()];
this.difficulty=4;
}
bigbang(){
const genesisBlock = new EzBlock('ANCESTOR','0000');
return genesisBlock;
}
}
|
区块的数据可以有很多种形式,当添加账号、时间戳、记录等数据和对应算法时,它就能实现类似账本、货币的功能。但无论区块链的功能如何丰富,它首先要实现的是它数据的完备性,而这种完备性由对哈希算法的应用实现。
哈希(Hash)算法,即散列函数。它是一种单向密码体制,即它是一个从明文到密文的不可逆的映射,只有加密过程,没有解密过程。同时,哈希函数可以将任意长度的输入经过变化以后得到固定长度的输出。哈希函数的这种单向特征和输出数据长度固定的特征使得它可以生成消息或者数据。
简单来说,哈希能对任意输入生成近似唯一的结果,所以常常以类似”指纹”的功能使用。就像用指纹认定一个特殊的人一样,hash值能用来检验数据是否被篡改。
checkHashValid(){
if(this.chain.length===1){
if(this.chain[0].hash !== this.chain[0].createHash()){
return false;
}
return true
}
else {
const chainLength = this.chain.length;
for(let i=0;i<chainLength-1;i++){
if(this.chain[i].hash !== this.chain[i].createHash()){
console.log("区块数据与hash值不匹配")
return false;
}
const previousBlock = this.chain[i];
if(this.chain[i+1].previousHash !== previousBlock.hash){
console.log("前后hash值冲突")
return false;
}
}
console.log('非常好区块链')
return true;
}
}
|
上一段代码将保证区块内、区块之间的数据完备性,特别是当有人想篡改数据时,他往往需要从他想改的节点沿着链一直修改到最新的节点,这将大大增加修改的成本。
去中心化的系统
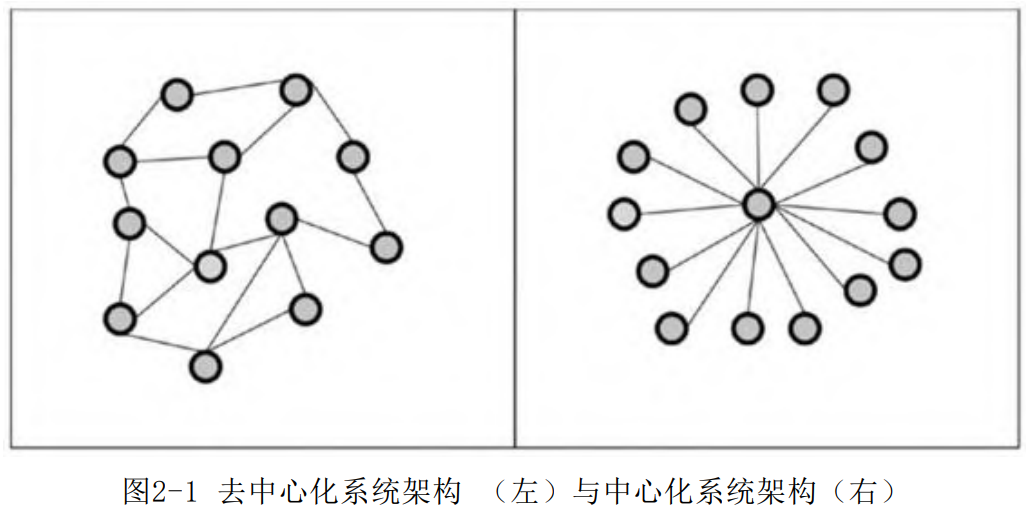
所有点对点系统的用户都是提供服务和使用服务的人,并且他们之间的交易和共享没有中间人。但也导致他们的行为往往缺乏监管,所以区块链在传播的过程中一定会被检验。篡改区块链的成本不只是技术上修改一大条区块的难度,还有消除所有用户对修改者和数据的质疑。
简单使用区块链
new一个试试,基于前面给出的代码(且在它只运行在你一个用户的情况),你可以尝试随意的添加区块,输出他们。(暂时没有给出向EzChain添加区块的函数,可以参考以下代码并记得篡改前后的hash值使他们不会被check出错误)
let anyBlock = new EzBlock('i wanna eat spicy food','none previous')
const anyEzChain = new EzChain()
anyEzChain.chain.push(anyBlock)
anyEzChain.checkHashValid()
|
很没意思,因为区块被你随意地修改添加,不免觉得这区块又不安全、也不珍贵。试图将它变得珍贵些吧。
getLatesetBlock(){
return this.chain[this.chain.length-1];
}
appendBlocktoChain(){
let newBlock= new EzBlock()
newBlock.previousHash = this.getLatesetBlock().hash
newBlock.data = Math.random().toString()
newBlock.data += this.proofOfWork(newBlock.data)
newBlock.hash = newBlock.createHash()
this.chain.push(newBlock);
}
proofOfWork(dataneeded){
if(isNaN(this.difficulty)){
return null;
}
let data = dataneeded
let x = 1;
let substr='0';
let temp=this.difficulty
while(--temp){
substr+='0'
}
console.log(substr)
while(true){
if(getSha(data+x).toString().substring(0,this.difficulty)!==substr){
x = x+1;
}else{
console.log(getSha(data+x).toString())
console.log(x);
break;
}
if(x%100000==0){
console.log(x)
}
}
console.log("end of POW");
return x;
}
const anyEzChain = new EzChain()
anyEzChain.appendBlocktoChain()
anyEzChain.appendBlocktoChain()
anyEzChain.appendBlocktoChain()
anyEzChain.appendBlocktoChain()
anyEzChain.checkHashValid()
console.log(anyEzChain)
|
添加区块的方法变得很复杂,而且体感上运行的时间变长了特别多(如果你尝试将anyEzChain.difficulty增加到8以上会明显更多)。这涉及到POW(proofOfWork,即工作量证明),它将增加添加区块的成本,当你想增加这个成本时。
工作量证明
哈希算法的特殊性也可以形成只有计算机运算才能解决的问题,称为哈希难题。

解答哈希难题只能够不断去试错。首先要猜一个随机数,并计算数据与随机数构成的数据集合的哈希值,然后根据限制条件去评估得到的哈希值。如果哈希值满足这些限制条件,你就成功解决了这个哈希难题。整个解题的过程就是工作量证明。
过渡到虚拟货币
普通的区块链已经有部分虚拟货币的特性。假设我要发行一个简单的虚拟货币(叫他Stupid Coin),发行的对象是我自己。以上面的所有代码为例,发行的方法就是
const anyEzChain = new EzChain()
我需要我自己去挖矿,挖矿的方法是
anyEzChain.appendBlocktoChain()
在等待很多个小时后我终于挖到了一个币。假设有另一个我自己,他也在和我同时挖币,但可惜的是这个币只被我挖到了。他高度怀疑我是伪造的假币而不是自己挖的,所以他尝试验证这个币的有效性,方法是
anyEzChain.checkHashValid()
他用远小于挖鼻的时间验证了我的币保不保真。最终他只能气急败坏地去挖下一个。
挖鼻的过程大抵如此,只不过为了让所有人愿意检验别人挖到的币,所有检验别人挖到币的人都能获得相应的奖励。这份奖励又挖到币的人提供。
多人同台激情交易
想象很多人都在使用我的傻币,但我的币十分特殊简陋,没有人知道自己手上的币是新币还是老币(因为使用的人太多)很多人于是拿老币伪装新币卖给别人,还一币多卖。
我为了保障用户的交易体验,决定给每个币添加一个交易记录,为了防止这个账本被修改,我再次使用了hash和检验算法
important:以下代码和前文应该区分开
const getsha=require("crypto-js/sha256")
const eclib = require('elliptic').ec
const ec = new eclib('secp256k1')
class Transaction {
constructor(from,to,amount){
this.from = from
this.to = to
this.amount = amount
}
sign(key){
this.signature = key.sign(this.computeHash(),'base64').toDER('hex')
}
computeHash(){
return getsha(this.from+this.to+this.amount).toString()
}
isValid(){
if(this.from == null){
return true
}
if(!this.signature)
throw new Error('sig missing')
const publicKey = ec.keyFromPublic(this.from,'hex')
return publicKey.verify(this.computeHash(),this.signature)
}
}
class cryptoBlock {
constructor(transactions,previousHash){
this.transactions = transactions
this.previousHash = previousHash
this.timestamp = Date.now()
this.nonce = 1
this.hash = this.computeHash()
}
computeHash(){
return getsha(JSON.stringify(this.transactions)+this.previousHash+this.nonce).toString()
}
getAnwser(difficulty){
let anwser = ''
for(let i=0;i<difficulty;i++){
anwser+='0'
}
return anwser
}
mine(difficulty){
if(!this.validateTransact()){
throw new Error('交易异常,不准挖')
}
while(true){
this.hash = this.computeHash()
if(this.hash.substring(0,difficulty)!=this.getAnwser(difficulty)){
this.nonce++
this.hash = this.computeHash()
}else{
break
}
if(this.nonce%1000===0){
console.log(this.nonce)
}
}
console.log("挖矿结束XD",this.hash)
}
validateTransact(){
for(let transaction of this.transactions){
console.log(transaction)
if(transaction.signature&&!transaction.isValid()){
return false
}
}
return true
}
}
|
代码内引入了对交易记录的签名,对区块的时间戳和挖矿次数记录。为什么会多此一举?
考虑到虚拟货币的特殊性和保证去中心式系统正常运转等因素下,发行者总有很多不得不保证的功能。例如:
- 减少网络延迟或丢失产生的影响,如双花问题等。
- 能够投票决定被所有人接受的账本数据,如分布式共识的保证
- 对造假等行为的惩罚和维护环境的奖励
这些都是保证账本的不可修改性所使用的,而单一的哈希指纹并不能完全保证这一点。
为什么账本需要这么严格的保护?转一个例子(from什么是51%算力攻击? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
上述的例子使用最长链共识作为共识标准。攻击者能够通过修改账本实现多次交易已经被交易的区块。而事实上因为修改账本的成本太高,以及破坏区块链所在的生态百害无利的基础上,往往没有人实施这种攻击。
完善未完成的链
下面的代码仍然是以我自己为发行者和唯一使用者来写的。总体和EzChain区别不大。
const getsha=require("crypto-js/sha256")
const eclib = require('elliptic').ec
const ec = new eclib('secp256k1')
class Chain {
constructor(difficulty){
this.chain = [this.bigbang()]
this.transactionsPool = []
this.minerReward = 50
this.difficulty = difficulty
}
setDifficulty(difficulty){
this.difficulty = difficulty
}
bigbang(){
const genesisBlock = new cryptoBlock("ANCESTOR","")
return genesisBlock
}
getLatestBlock(){
return this.chain[this.chain.length-1]
}
appendBlockToChain(newblock){
newblock.previousHash = this.getLatestBlock().hash
newblock.mine(this.difficulty)
this.chain.push(newblock)
}
addTransToPool(transaction){
console.log(transaction)
if(!transaction.from||!transaction.to){
throw new Error('invalid addr')
}
if(!transaction.isValid()){
throw new Error('invalid signature')
}
this.transactionsPool.push(transaction)
}
mineTransactionPool(minerRewardAddress){
const rewardTranssaction = new Transaction(
null,minerRewardAddress,
minerRewardAddress,
this.minerReward
)
this.transactionsPool.push(rewardTranssaction)
const newBlock = new cryptoBlock (
this.transactionsPool,
this.getLatestBlock().hash
)
newBlock.mine(this.difficulty)
this.chain.push(newBlock)
this.transactionsPool = []
}
checkChainValid(){
if(this.chain.length===1){
if(this.chain[0].hash !== this.chain[0].computeHash()){
return false
}
else {
return true
}
}else {
const chainLength = this.chain.length
for(let i=0;i<chainLength-1;i++){
if(this.chain[i].hash!==this.chain[i].computeHash()){
console.log('block not complete')
return false
}
const previousBlock = this.chain[i]
if(this.chain[i+1].previousHash !== previousBlock.hash){
console.log('not same between bros')
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
validateChain(){
if(this.chain.length === 1){
if(this.chain[0].hash !== this.chain[0].computeHash())
{
return false
}
return true
}
for(let i=0;i<=this.chain.length-1;i++){
const blockToValidate = this.chain[i]
if(!blockToValidate.validateTransact()){
console.log('illeagal transaction')
return false
}
if(blockToValidate.hash !== blockToValidate.computeHash()){
console.log('数据篡改')
return false
}
const previousBlock = this.chain[i-1]
if(previousBlock&&blockToValidate.previousHash !== previousBlock.hash){
console.log("前后区块链断裂")
return false
}
}
return true
}
}
module.exports = { Chain, Transaction, cryptoBlock }
|
其中添加了完整的添加并验证账本的检测
毕竟交易账本也应该和区块一样能被所有人验证
签名的作用是为了每个人都能验证签名是你的并且转账也合法
这时的挖矿流程也有了一些变化

run it
const ecLib = require('elliptic').ec;
const ec = new ecLib('secp256k1')
const { Transaction, Chain, cryptoBlock } = require("./blockchainModule");
const luotuoCoin = new Chain(3);
const keyPairSender = ec.genKeyPair();
const privateKeySender = keyPairSender.getPrivate('hex')
const publicKeySender = keyPairSender.getPublic('hex')
const keyPairReceiver = ec.genKeyPair();
const privateKeyReceiver = keyPairReceiver.getPrivate('hex')
const publicKeyReceiver = keyPairReceiver.getPublic('hex')
const t1 = new Transaction(publicKeySender, publicKeyReceiver, 10);
t1.sign(ec.keyFromPrivate(privateKeySender))
console.log(t1)
luotuoCoin.addTransToPool(t1);
luotuoCoin.mineTransactionPool("addr3");
console.log(luotuoCoin.validateChain())
console.log(luotuoCoin)
console.log(luotuoCoin.chain[1])
|
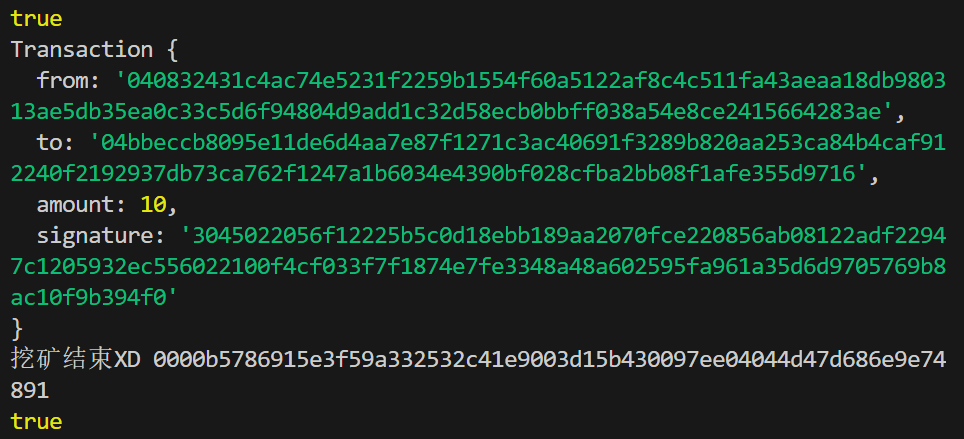
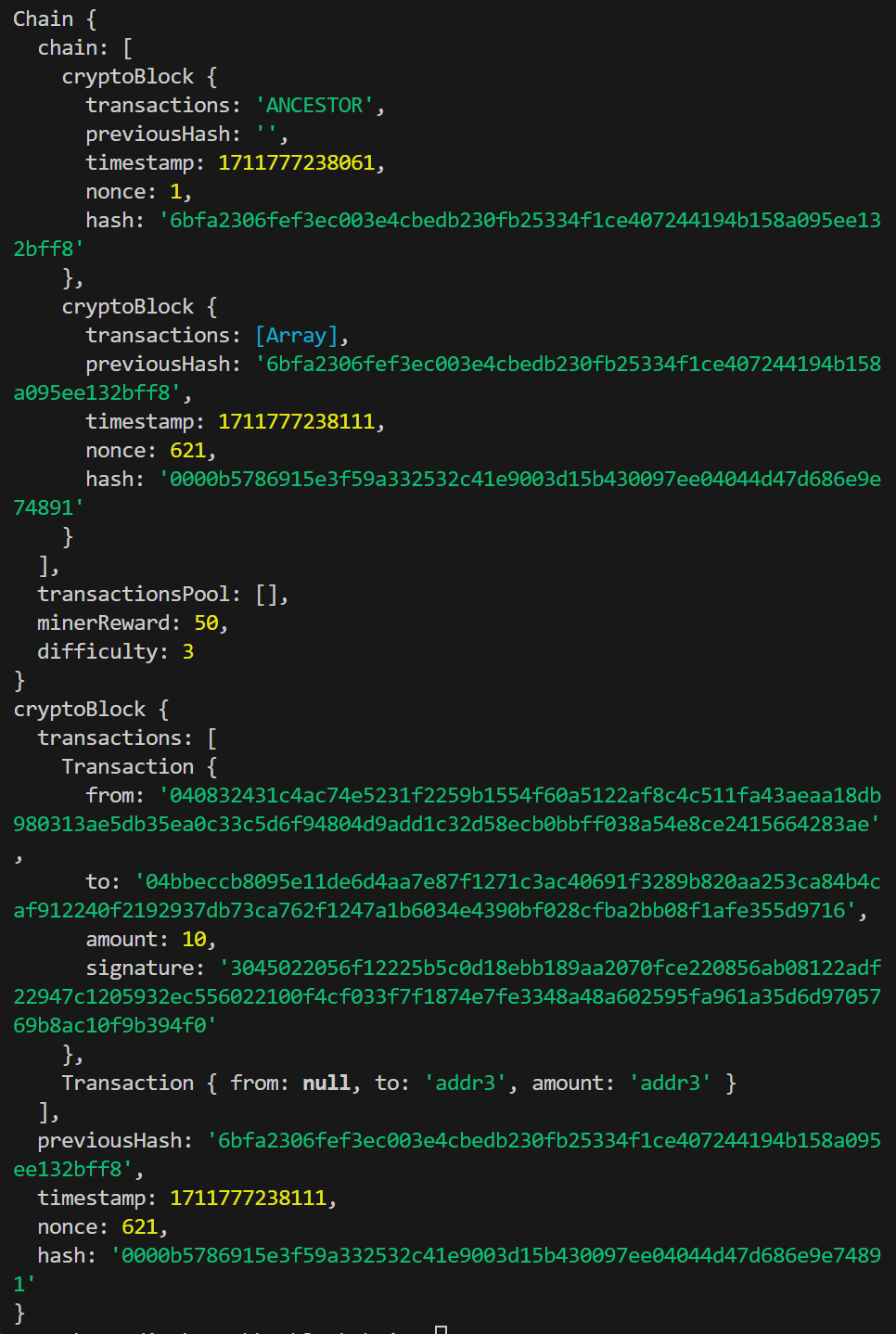
以下是执行结果的数据展示
参考:
- bilibili的BV14E411v7eS,落拓佬的视频
- 区块链基础知识25讲





